Adeno-associated virus (AAV) is a small non-enveloped virus which requires a helper virus for active replication. AAV is used as a gene therapy vector because they are non pathogenic, they persistently express the transgene in the transduced cells, and can transduce both dividing and non-dividing cells. In humans, the presence of serum antibodies directed against AAV vector serotypes is a major drawback for the use of AAV as a gene therapy vector. Reports suggest that neutralizing antibodies against a serotype of AAV can reduce the efficiency of the gene delivery of the vector. Hence, screening for AAV serotype specific antibodies in potential gene therapy individuals is of paramount importance. Screening of AAV serotype specific antibodies is done mainly by transduction inhibition assay (TIA). ELISA is being used for screening of total antibodies against AAV serotypes using AAV capsids. However, this format (using whole capsid protein) does not give information on Serotype-specific detection of AAV antibodies. In this component of the NAHD project, we would first establish a peptide ELISA for the detection of serotype-specific antibodies against AAV and compare the results with TIA which is the gold standard for the detection of neutralizing antibodies against AAV. This study would help us establish a good method of screening for AAV antibodies. Also, we would be able to assess the prevalence of antibodies against different serotypes of AAV in the Indian population.
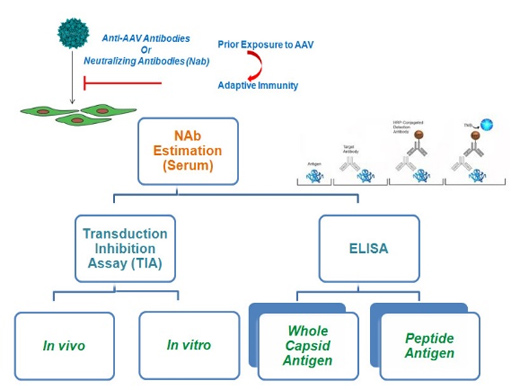
Figure 1: AAV antibody detection methods. Transduction inhibition assay detects only neutralizing antibodies. ELISA using whole capsid detects both neutralizing and binding antibodies. Peptide ELISA detects either neutralizing or binding antibodies.

Figure 2: In vitro transduction inhibition assay to assess neutralizing antibodies in plasma samples. Plasma samples were diluted at different dilutions and mixed with AAV vectors containing a reporter gene. Plasma + AAV vector was allowed to transduce in cell lines and expression of the reporter gene evaluated after 48 hours. Positive control is sample containing AAV neutralizing antibody. Negative control is sample negative for AAV neutralizing antibodies. Titer of a sample is the highest dilution at which there is ≥50% inhibition of transduction compared to no serum control (Negative control).

